Osteochondrosis is a disease of the spine, the main symptom of which is the lowering of the intervertebral discs and the cessation of work on them.
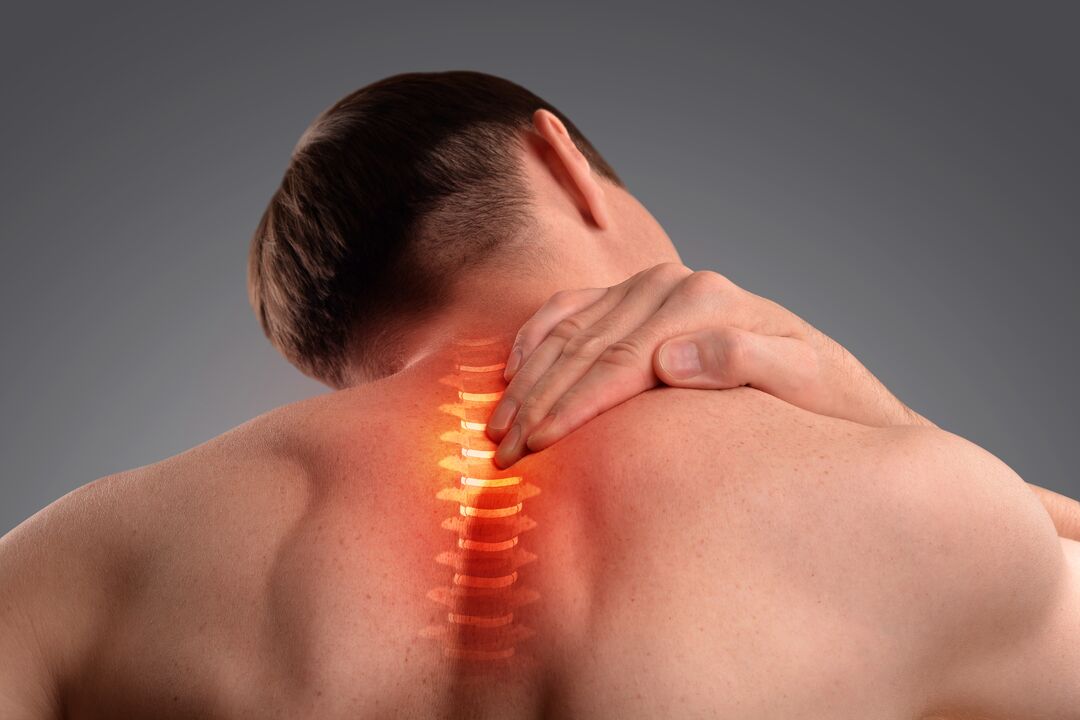
Osteochondrosis is a very common disease in people of different ages. In men and women, back pain most often manifests itself at the age of 40 years. In old age, osteochondrosis affects 90% of the population. The most common type of such a disease is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. We will talk about it.
Causes of osteochondrosis
When the aging process begins, the functions of blood vessels, bones and cartilage deteriorate; with all these indicators, the body still does not get enough vitamins, which worsens the process.
But there are also reasons not related to aging, due to which the disease may appear earlier than usual.
- Excess weight. Causes metabolic disorders and overloads the intervertebral disc.
- Inheritance.
- Injury.
- Passive lifestyle. As well as staying in one position for a long time (driving).
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system (flat feet, poor posture). Due to such diseases, the load on the spine is uneven.
- Strong stress in the spine (multiple pregnancies).
Signs of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
This type of osteochondrosis manifests more often than others. This was due to the fact that the cervical vertebrae are located very close to each other and have a different structure from other vertebrae.
Why are the cervical vertebrae displaced? This is due to their age-related fragility and poor development of the muscular frame of the neck.
In addition to pain, arteries or a nerve bundle can also be compressed by displacement of the cervical vertebrae. Due to pain of different localization, osteochondrosis can be confused with other diseases.
Here are other symptoms of osteochondrosis:
- Pain in different parts of the body. In the heart region, the back of the head, neck, shoulders and shoulders. There may also be weakness in the arms and problems with extending the arms to the sides. This is due to the tight nerves in the cervical spine.
- Numbness in the fingers. Sensation of tingling in the fingertips and low sensitivity of the hands.
- Discomfort when turning your head. Cracking of the vertebrae, lumbago in the neck, dizziness, heaviness in the head or shortness of breath. If these symptoms are particularly acute during sports, this indicates the initial stage of osteochondrosis development. All of the above comes from the appearance of bone formations in the neck.
- Vision problems. Deterioration of vision, fog or black spots that tremble. This indicates a late stage of osteochondrosis and arises from an insufficient amount of blood in the brain.
- Discomfort in the throat. The feeling of a lump in the throat, sweating and difficulty in swallowing are signs of the initial stage of development of osteochondrosis. Frequent nausea may also occur.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
What happens during treatment?
Under X-ray control, needles are inserted into the aspect joints of the cervical spine. Through them, two drugs are injected into the affected joints: a local anesthetic, which relieves pain, and a hormone, which will further relieve inflammation in the problem area.
This blockage can provide relief for quite a long time. However, if the pain has returned, provided the blockage has a positive effect, it is possible to perform radiofrequency ablation of the nerves that remove the pain from the joints in the future.
Such a procedure is always performed only in the second stage and leads to a lasting positive effect (from one to several years).
What are the advantages of this type of treatment for osteochondrosis?
- It does not require general anesthesia and lasts no more than an hour.
- The patient can go home within a few hours after the procedure.
- Minimal risk of complications.
- Weak and elderly patients can also be treated in this way.
- The recovery period does not exceed 2 days.
To speed up the recovery process, we recommend that you undergo a course of exercise therapy after surgery. This is a type of therapy that involves certain physical activities after surgery. All exercises are selected individually by the attending physician.



















